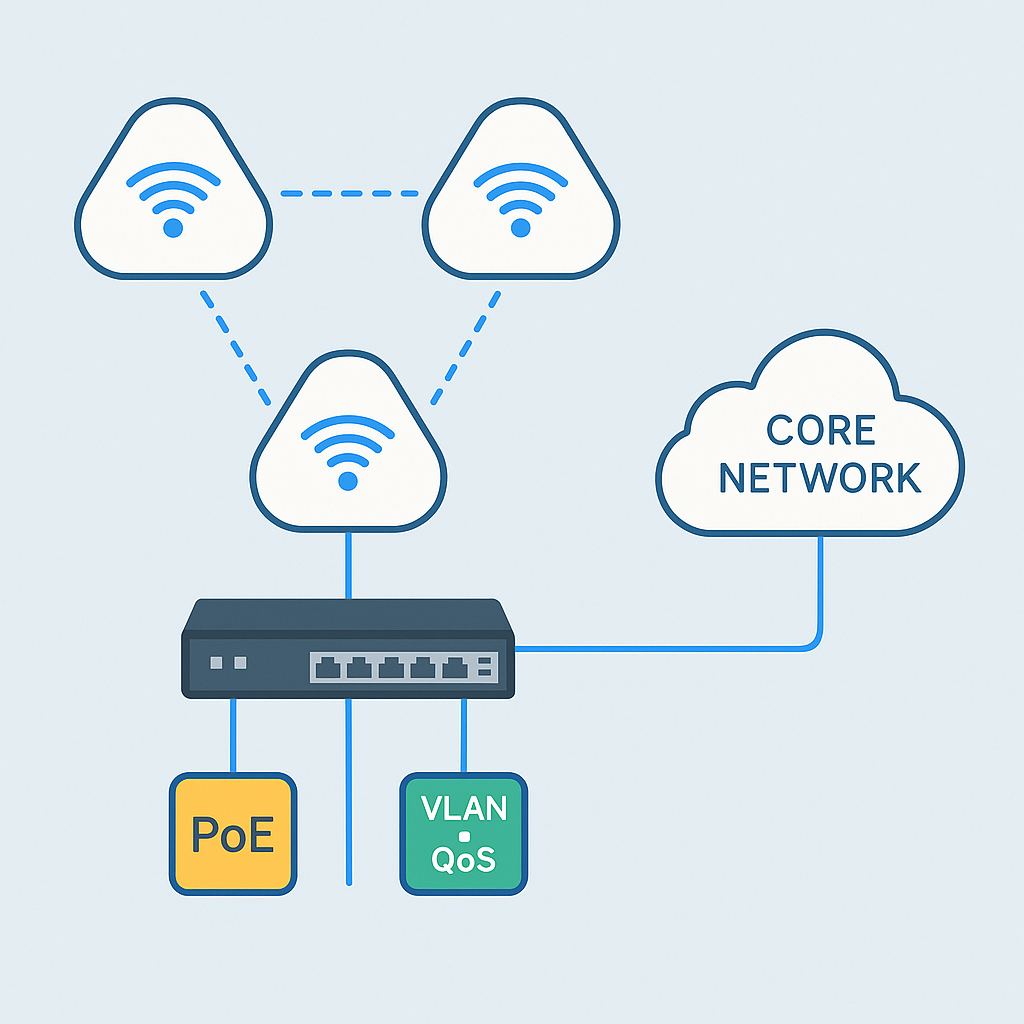
As enterprises move toward wireless coverage, mesh Wi-Fi has become the architecture of choice for campuses, factories, hotels, and multi-building locations. Mesh nodes and access points create flexible radio pathways within a site, but the wired edge—where these radios connect—is equally critical. Network switches act as the backbone, transforming a group of mesh radios into a resilient and manageable enterprise network. This article explains the practical role of switches in a mesh environment and how Toda helps procurement and IT teams deploy scalable, secure, and high-performance mesh solutions.
Why Switches Are Important in Mesh Networks
Mesh networks coordinate radios and wireless links to achieve coverage without running cables to every endpoint. However, each mesh node still relies on wired infrastructure for power, backhaul aggregation, management, and security. Switches provide:
Power (PoE) — Power over Ethernet (PoE) simplifies deployment by providing both data and power to mesh nodes and access points (APs). Industrial and enterprise-grade PoE switches eliminate the need for local power supplies at each node, reducing installation time and costs.
Aggregation backhaul – The switch collects traffic from multiple mesh nodes and forwards it to the data center or internet gateway. High-capacity uplinks (multi-gigabit or fiber) prevent the wired side from becoming a bottleneck.
Segmentation and Security – VLANs applied on the switch isolate management, guest, IoT, and corporate traffic. Switch-level access control lists and port security prevent lateral movement and control risks introduced at the wireless edge.
Quality and Prioritization – QoS policies configured on the switch ensure that voice, video, and critical IoT telemetry receive priority across both wired and wireless domains.
Resilience and Redundancy – Link Aggregation (LACP), redundant uplinks, and STP/RSTP/shorter convergence protocols maintain connectivity in the event of link or device failure.
Centralized Management – Managed switches provide SNMP/NetConf/RESTful API hooks to the same NMS or controller used to manage mesh nodes, enabling unified monitoring and automated workflows.
Typical switch roles in a mesh deployment
Access/Edge Switches
Edge switches are deployed in ceiling voids, independent fabric layouts (IDFs), or outdoor cabinets to provide PoE power to access points (APs) and mesh nodes. They typically support 1GbE to multi-gigabit ports, have a PoE budget commensurate with the number of radios, and include features such as LLDP-MED for automatic access point discovery.
Distribution/aggregation switches
These switches sit a layer above the edge, aggregating traffic from dozens of edge switches. They typically offer higher throughput, SFP+/10GbE uplinks, and more robust routing/ACL capabilities for traffic diversion or policy enforcement.
core switch
The core is responsible for inter-VLAN routing, firewall links, and high-capacity transport to the data center or cloud controller. In large mesh network deployments, the core must handle multicast video, centralized authentication, and analytics streams generated by wireless assets.
Outdoor and Rugged Switches
For mesh nodes mounted on utility poles or outside buildings, industrial PoE switches with wide temperature ranges, surge protection, and weatherproof housings ensure proper operation in harsh environments.
Best Practices for Switch Selection in Mesh Wi-Fi
Match PoE budget to radio requirements: Wi-Fi 6/6E APs and mesh radios typically require PoE+ or PoE++; adjust switch power budgets to avoid mid-deployment surprises.
Multi-gigabit uplinks where needed: High-density areas and backhaul aggregation points benefit from 2.5/5/10 GbE ports or fiber SFP+ links.
Use managed switches: VLANs, QoS, port security, and telemetry are critical for enterprise mesh deployments—unmanaged switches leave you blind and vulnerable.
Redundancy plan: Design uplink and switch locations so that a single switch or fiber cut does not isolate an entire floor or building.
End-to-end monitoring: Use a single management plane whenever possible to correlate RF events and wired performance for faster troubleshooting.
Protect the edge: Implement 802.1X and port security on switch ports connected to mesh nodes to prevent unauthorized devices from joining the network.
How Toda Designs Switch-Enabled Mesh Solutions
Toda’s approach combines industrial-grade mesh APs with a switch architecture, focusing on delivering real results for B2B customers:
Site-driven design: Toda begins by conducting a site survey and heat map simulation to determine the number, type, and location of mesh nodes and the switch layers required to support them.
Power and bandwidth planning: Engineers determine PoE budgets and uplink capacity to support peak traffic and future growth, avoiding unexpected bottlenecks.
Security Design: Toda templated VLANs, 802.1X policies, and ACLs into switch configurations and deployed them uniformly across sites. This reduced risk and accelerated deployment.
Resilience and Maintenance: Switch stacking, LACP configuration, and redundant uplinks are standard features in Toda’s enterprise-class SLA design. Remote management and automated alerts reduce truck rolls and improve mean time to repair.
End-to-end lifecycle: From procurement and configuration to phased firmware upgrades and performance tuning, Toda provides services to ensure the health of your mesh network for many years.
Real-world use cases
University campus: Students, faculty, and IoT sensors require segmented access between dormitories, lecture halls, and outdoor courtyards. Toda’s Mesh APs connect to PoE edge switches; the distribution switches aggregate and route traffic to the campus core, while maintaining isolation between guest and research networks.
Smart Factory: Automated guided vehicles and inspection cameras rely on low latency and deterministic paths. Rugged outdoor switches provide PoE to mesh nodes throughout the production floor; QoS and VLAN features on the switches ensure that real-time control traffic receives priority.
Hospitality and Food Service: Meeting rooms and public areas experience high traffic density, requiring multi-gigabit uplinks and per-SSID bandwidth policies. Toda configured edge switches to divert guest traffic to a separate VLAN and captive portal, while retaining back-office connectivity for employees.
Purchasing considerations for B2B buyers
When sourcing switches for a mesh project, buyers should evaluate:
Power capabilities (PoE/PoE+/PoE++) and per-port power guarantee
Port speeds and available uplink options (SFP/SFP+/Multi-Gigabit)
Management capabilities (VLAN, ACL, QoS, SNMP, API access)
Ruggedized for outdoor or industrial deployment
Vendor Support – Firmware lifecycle, documentation, and global logistics
Toda works with procurement teams to produce detailed BOMs, configuration templates, and deployment roadmaps so integrators and internal teams can execute with confidence.
in conclusion
Mesh Wi-Fi offers flexible coverage and simplified radio planning, but the wired switching layer is the unsung hero that enables enterprise-grade mesh networks: it provides power, aggregated backhaul, segmentation, QoS, and resiliency. For overseas B2B customers seeking a reliable, scalable wireless infrastructure, Toda combines market-proven mesh APs with carefully designed switch architectures and professional services to help enterprises deploy wireless networks that meet their real-world operational needs.
Ready to design an end-to-end mesh Wi-Fi network? Contact Toda for a customized site assessment, migration recommendations, and a deployment plan targeted for scale and security.
Post time: Aug-29-2025