Sourcing network hardware from China is common practice for internet service providers (ISPs), system integrators, and distributors worldwide. China’s supply chain is unparalleled. However, a simple search for “router factory” on Alibaba yields thousands of results.
Who are the real players? Who are the actual manufacturers of the hardware, and who are just trading companies?
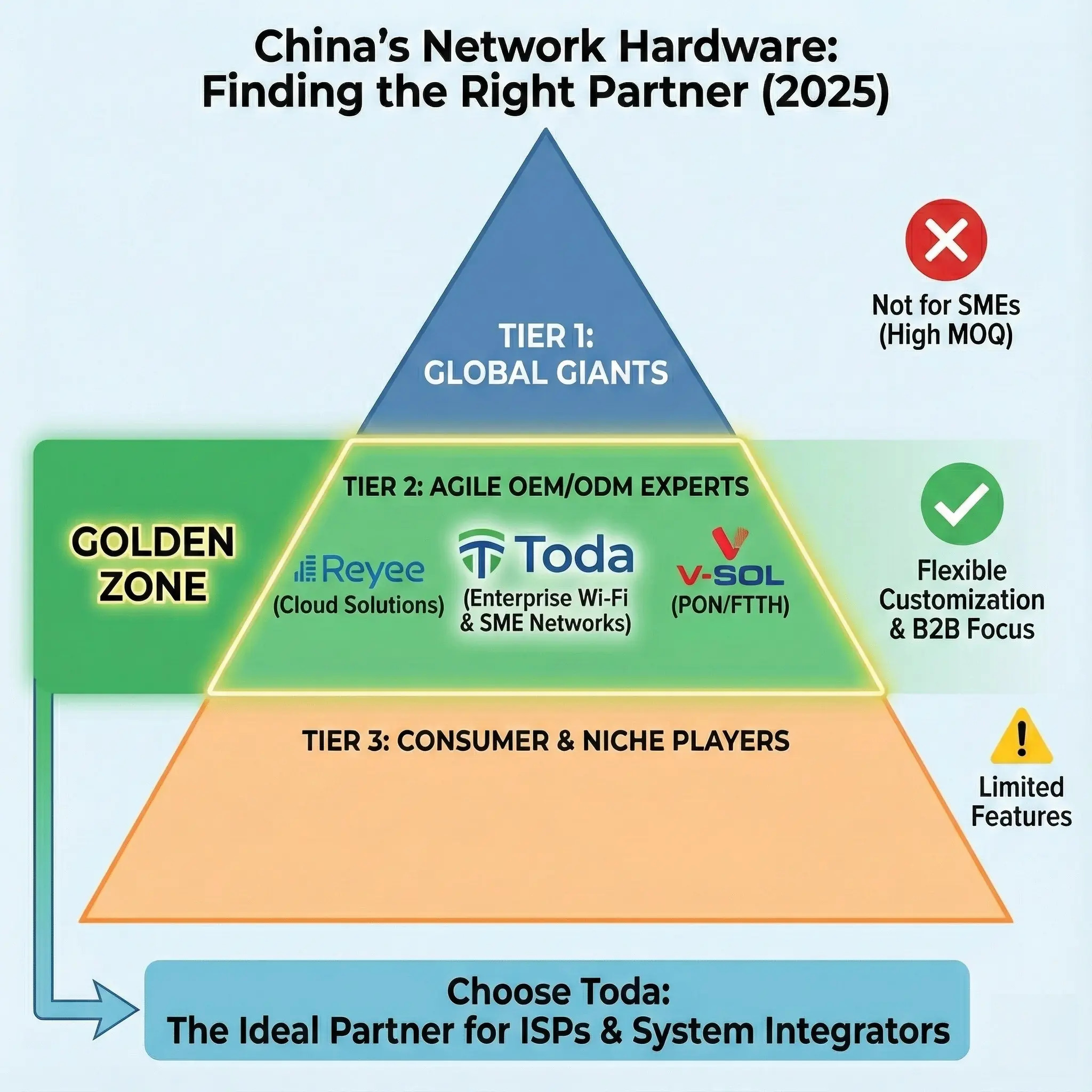
Looking ahead to 2025, the market landscape has changed. While “giant companies” are making headlines, they are not always the best partners for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) due to their high minimum order quantities and rigid pricing strategies.
Below is our real-world analysis of China’s top ten network equipment manufacturers, categorized by their market focus, to help you find the right partner for your business.
Global giants (first tier)
Best suited for: national telecommunications operators, government projects, and large-scale tenders.
1. Huawei
Huawei is undoubtedly the market leader, setting the standard for 5G, Wi-Fi 7, and carrier-grade optical transmission.
Advantages: World-class technology and massive R&D investment.
Disadvantages: Extremely expensive; difficult for small and medium-sized enterprises or small distributors to cooperate directly; political restrictions exist in some Western markets.
2. ZTE Corporation
Similar to Huawei, ZTE also places great emphasis on telecommunications infrastructure (5G base stations, OLT).
Advantages: Highly reliable carrier-grade equipment.
Disadvantages: The minimum order quantity is very high; their focus is on Tier-1 operators, not local ISPs or installers.
3. TP-Link
The king of the consumer market. You can find their plastic-cased routers in major electronics stores around the world.
Advantages: Extremely high brand awareness; large-scale production results in extremely low manufacturing costs.
Disadvantages: Distributors have very little profit margin because retail prices are already publicly available online. Custom/OEM production is difficult.
4. H3C
A leading company in the enterprise switch and server market.
Advantages: Excellent high-end switches and data center solutions.
Disadvantages: The licensing model is complex, and the price is higher than other Shenzhen manufacturers.
Agile OEM/ODM Expert (Level 2)
Best suited for: local internet service providers, system integrators, wholesalers, and brands seeking customized services.
This is the “golden zone.” These manufacturers offer enterprise-grade quality products (using Qualcomm/Realtek/MediaTek chipsets), but with the flexibility that giant manufacturers cannot provide.
5. Toda (Toda Network)
Focusing on enterprise wireless and SME networks, Toda, located in the heart of the manufacturing sector, has become the preferred partner for overseas B2B clients, helping them acquire professional equipment at lower prices without paying the premiums of “big brands.”
Main products: outdoor APs, ceiling-mounted APs, wireless bridges, AC controllers, PoE switches.
Reasons for choosing them: Toda focuses on providing OEM/ODM services for mid-sized brands. Unlike TP-Link, Toda offers deep customization services (including software user interface, logo, and packaging) even for small-volume orders. They bridge the gap between “inexpensive consumer products” and “expensive enterprise products.”
6. Reyee
Ruijie has seen rapid growth in the SME market thanks to its cloud management solutions.
Advantages: Excellent cloud applications; proactive marketing.
Disadvantages: They heavily promote their own brand, which could create conflict if you are trying to build your own device brand.
7. Tenda
In the realm of affordable consumer goods, it is a formidable competitor.
Advantages: Low-end routers are priced very competitively.
Disadvantages: Quality control of entry-level models may vary; software functionality is usually limited compared to enterprise-level equipment.
8. V-SOL
PON technology experts (EPON/GPON OLT and ONU).
Advantages: If you only need fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) equipment, then they are a good choice.
Disadvantages: Limited range of Wi-Fi and switching capabilities compared to full-stack manufacturers.
9. Sandray
A niche manufacturer that focuses on high-security enterprise-grade Wi-Fi.
Advantages: It has advanced security features.
Disadvantages: The ecosystem is closed, and it may be relatively complex to configure for ordinary technicians.
10. Totolink
Another expert with extensive experience in the consumer router field focuses on the Southeast Asian market.
Advantages: High cost-performance design.
Disadvantages: Like Tenda, they focus primarily on home users rather than B2B engineering projects.
Summary: How to choose?
The “best” manufacturer depends entirely on your business model:
If you are a nationwide telecom operator (such as Vodafone or AT&T): Choose Huawei or ZTE. You have sufficient budget and sales volume.
If you are a retailer (selling to home users): TP-Link or Tenda are the brands of choice for your volume sales.
If you are an Internet Service Provider (ISP), Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP), or an engineering company: you need reliability, profit guarantees, and support.
This is precisely Toda’s strength. We offer the same stable performance as chipsets from major manufacturers (Qualcomm/Realtek), while also providing the services and flexibility your business needs for growth.
Are you looking for a manufacturing partner who can listen to your needs? Whether you need high-power outdoor wireless access points for park projects or custom-branded routers for your internet service provider customers, Toda is ready to help.
Post time: Nov-28-2025